Chapter 4
Cell Division and Mitosis

Courtesy of BA Education
Mitosis is the process in which the nucleus divides to form two identical nuclei. There are seven steps to mitosis including pre-mitosis, or interphase. The steps are interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis. A detailed description of each step is as follows:
Interphase
1) Cell grows. 5) Before duplicated, chromosomes are called chromatin and are long,
2) Cell develops and functions. thin, and threadlike.
3) Organelles divide. 6) Chromosomes duplicate.
4) Nucleolus and nuclear membrane 7) Chromosomes connect in the middle at centromere.
clearly visible.
Prophase
1) Mitosis begins! 4) Centrioles start to go to opposite ends of the cell. Stretchy, sticky
2) Nuclear membrane disintegrates. spindle fibers between them.
3) Nucleolus disintegrates. 5) Chromatids attach to sticky fibers at centromere.
Metaphase
1) All chromatids move to the middle of the cell.
2) Chromatids line up around the center (equator) of the cell.
Anaphase
1) Chromatids separate.
2) Each chromosome moves to opposite ends of the cell on spindle fibers as the fibers shrink.
Telophase
1) Mitosis ends. 4) Spindles go back to their original spot
2) Opposite of prophase. 5) Cell membrane starts to pinch in
3) Nuclear membrane and nucleolus reform. 6) Chromatids detach from sticky fibers
Cytokinesis
1) Cell membrane keeps pinching in until two identical daughter cells are formed.
Asexual reproduction allows one organism to produce one or more new organisms. Some different types of asexual reproduction are fission, budding, and regeneration. Fission allows organisms whose cells do not contain a nucleus to copy its genetic material and divide into two identical organisms. Budding occurs when an organism grows from the body of the parent organism. Regeneration is the process that uses cell division to grow new body parts
Interphase
1) Cell grows. 5) Before duplicated, chromosomes are called chromatin and are long,
2) Cell develops and functions. thin, and threadlike.
3) Organelles divide. 6) Chromosomes duplicate.
4) Nucleolus and nuclear membrane 7) Chromosomes connect in the middle at centromere.
clearly visible.
Prophase
1) Mitosis begins! 4) Centrioles start to go to opposite ends of the cell. Stretchy, sticky
2) Nuclear membrane disintegrates. spindle fibers between them.
3) Nucleolus disintegrates. 5) Chromatids attach to sticky fibers at centromere.
Metaphase
1) All chromatids move to the middle of the cell.
2) Chromatids line up around the center (equator) of the cell.
Anaphase
1) Chromatids separate.
2) Each chromosome moves to opposite ends of the cell on spindle fibers as the fibers shrink.
Telophase
1) Mitosis ends. 4) Spindles go back to their original spot
2) Opposite of prophase. 5) Cell membrane starts to pinch in
3) Nuclear membrane and nucleolus reform. 6) Chromatids detach from sticky fibers
Cytokinesis
1) Cell membrane keeps pinching in until two identical daughter cells are formed.
Asexual reproduction allows one organism to produce one or more new organisms. Some different types of asexual reproduction are fission, budding, and regeneration. Fission allows organisms whose cells do not contain a nucleus to copy its genetic material and divide into two identical organisms. Budding occurs when an organism grows from the body of the parent organism. Regeneration is the process that uses cell division to grow new body parts
Sexual Reproduction
Courtesy of MIT Department of Biology
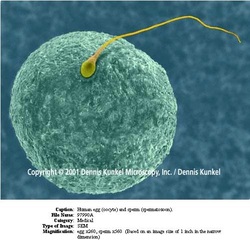
Sexual reproduction occurs when two sex cells, an egg and sperm, come together. Sperm is the male reproductive cell, and an egg is the female reproductive cell. When the egg and sperm's chromosomes join together, fertilization occurs. The fertilized cell is called a zygote.
Your body cells have forty-six chromosomes. Each chromosome has a match. There are twenty-three pairs of chromosomes in each cell. These cells are diploid cells.
Sex cells only have twenty-three chromosomes. They are called haploid cells because they have half the number of chromosomes your body cells do.
Some living things are polyploidy. This means that they have three or more sets of chromosomes. For example, bananas have three sets of chromosomes, and strawberries have six sets of chromosomes.
Your body cells have forty-six chromosomes. Each chromosome has a match. There are twenty-three pairs of chromosomes in each cell. These cells are diploid cells.
Sex cells only have twenty-three chromosomes. They are called haploid cells because they have half the number of chromosomes your body cells do.
Some living things are polyploidy. This means that they have three or more sets of chromosomes. For example, bananas have three sets of chromosomes, and strawberries have six sets of chromosomes.
DNA
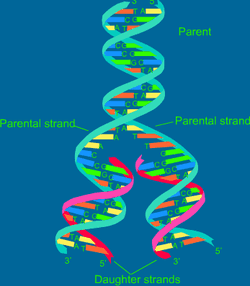
DNA(deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic material of all organisms. It is made up of two twisted strands of sugar-phosphate molecules and nitrogen bases.
DNA can be considered to look like a twisted ladder. The sides of the ladder are made up of sugar-phosphate molecules, and the rungs are made up of nitrogen bases. There are four different types of nitrogen bases: adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine. Adenine bases only matches with thymine bases, and guanine bases only match with cytosine bases. DNA needs to be copied. When this occurs, an enzyme separates the DNA sides. Then the new nitrogen bases pair with nitrogen bases on the original DNA strand. Finally, two identical DNA strands are created.
RNA is ribonucleic acid. It carries codes for making proteins from the nucleus to the ribosome. RNA also has nitrogen bases. Instead of the nitrogen base thymine, RNA has the nitrogen base uracil. Uracil matches with adenine. There are three types of RNA, rRNA(ribosomal), mRNA(messenger), and tRNA(transfer). The rRNA makes up the ribosome, the mRNA holds the code for making the protein, and the tRNA transfers amino acids to the ribosome. The most important thing about RNA is that it is involved in protein synthesis. Protein synthesis is the process in which the ribosome, with the help of RNA, makes proteins for the body.
DNA can be considered to look like a twisted ladder. The sides of the ladder are made up of sugar-phosphate molecules, and the rungs are made up of nitrogen bases. There are four different types of nitrogen bases: adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine. Adenine bases only matches with thymine bases, and guanine bases only match with cytosine bases. DNA needs to be copied. When this occurs, an enzyme separates the DNA sides. Then the new nitrogen bases pair with nitrogen bases on the original DNA strand. Finally, two identical DNA strands are created.
RNA is ribonucleic acid. It carries codes for making proteins from the nucleus to the ribosome. RNA also has nitrogen bases. Instead of the nitrogen base thymine, RNA has the nitrogen base uracil. Uracil matches with adenine. There are three types of RNA, rRNA(ribosomal), mRNA(messenger), and tRNA(transfer). The rRNA makes up the ribosome, the mRNA holds the code for making the protein, and the tRNA transfers amino acids to the ribosome. The most important thing about RNA is that it is involved in protein synthesis. Protein synthesis is the process in which the ribosome, with the help of RNA, makes proteins for the body.